Understanding VPS and VPN: What They Are and When to Use Them.
In the world of online technology, VPS (Virtual Private Server) and VPN (Virtual Private Network) are two terms that are often used interchangeably, even though they represent two very different solutions. While they both offer users a private and secure online experience, they do so in different ways and for different purposes. In this article, we will explore what VPS and VPN are, and when to use them.
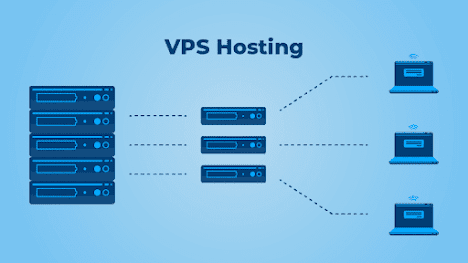
VPS- Virtual
Private Server
A VPS is a type of server that is divided into multiple virtualized compartments, each acting as an independent server with its own resources, operating system, and applications. This allows users to have complete control over their virtual environment, without the need to share resources with other users.
VPS
is ideal for individuals or businesses who require greater control over their
server environment. With a VPS, users can install any software or application
they need, customize their settings, and have full root access to the underlying
operating system. VPS is also a popular choice for web developers, who need a
private server environment to test and deploy their web applications.
VPN- Virtual
Private Network
VPNs are
commonly used to:
- Protect online
privacy by masking the user's IP address and encrypting their internet
traffic.
- Securely access
remote resources, such as company networks or cloud services, without
exposing sensitive information to outside threats.
- Bypass
geo-restrictions and access online content that is blocked in the user's
country.
VPNs
are a popular choice for individuals who want to protect their online privacy
and security, as well as businesses that need to provide secure remote access
to their employees.
When to use VPS vs VPN
VPS
and VPN are two different things that serve different purposes.
A
VPS, or Virtual Private Server, is a type of hosting service that provides a
virtual machine that is dedicated to a single user, giving them full control
over the operating system and installed software. VPS hosting is commonly used
for hosting websites, web applications, and other online services.
A
VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a technology that allows you to connect to
the internet securely and privately by encrypting your internet traffic and
routing it through a remote server. VPNs are commonly used to protect your
online privacy and security, bypass geo-restrictions, and access content that
may be blocked in your region.
Here
are some situations where you might use VPS vs VPN:
- Use a VPS when you
need to host a website, web application, or other online service that
requires a dedicated server with full control over the operating system
and installed software.
- Use a VPN when you
need to secure your internet connection, protect your online privacy, or
bypass geo-restrictions. This could be useful when you are accessing the
internet from a public Wi-Fi network, or when you want to access websites
or services that are blocked in your region.
To
remotely access a VPS (Virtual Private Server) or a VPN (Virtual Private
Network), you will need to use different tools depending on your specific
situation and requirements.
If
you want to access a VPS, you will typically need to use an SSH (Secure Shell) client. SSH is a secure protocol that allows you to connect to a remote server
over the internet and access its command-line interface. There are several SSH
clients available, such as PuTTY, OpenSSH, or MobaXterm, that you can use to
access your VPS.
If you want to access a VPN, you will typically need to use VPN client software. This software will allow you to connect to a VPN server and create a secure connection between your local computer and the remote network. The specific software you use will depend on the type of VPN you are connecting to. For example, if you are connecting to a corporate VPN, you may need to use a client provided by your employer. If you are connecting to a public VPN service, you may need to use a client provided by the service provider.



Comments
Post a Comment